hardness test theory|principle of hardness tester : online sales The Brinell hardness test is an empirical indentation hardness test that can provide useful information about metallic materials. This information may correlate to tensile strength, wear resistance, ductility, and other physical characteristics of metallic materials, and may be useful in quality control and selection of materials. webICQ New: Solo niñas videos e imágenes
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da Package Approved. This package was approved by moderator Windos on 19 Aug 2021. Description. The Microsoft XNA Framework Redistributable download provides game developers with the XNA Framework run-time libraries they can include with their product for redistribution on the .
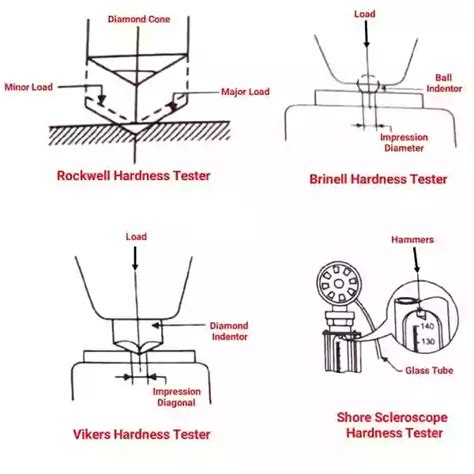
Hardness is the mechanical resistance of a material (specimen) to mechanical indentation by another harder body (indenter). The hardest natural material is the diamond, which is used for the indenter (industrial diamond).The principle of electronically controlled and permanently monitored load application .The Brinell hardness test is an empirical indentation hardness test that can provide useful information about metallic materials. This information may correlate to tensile strength, wear resistance, ductility, and other physical characteristics of metallic materials, and may be useful in quality control and selection of materials.II. Theory and Principle of the Rockwell Hardness Test. The Rockwell Hardness Test uses a depth-differential method to test for hardness. A predetermined minor load is applied to the test sample, and the depth measurement is taken. Then a major load is applied to the same spot, which creates a deeper indentation.
The Rockwell hardness test was invented in 1914 by Hugh and Stanley Rockwell. It measures the hardness of materials by applying two loads with an indenter and measuring the depth of penetration. There are different .The Vickers hardness test follows the brinell principle, in that an indenter of definite shape is pressed into the material to be tested, then the load is removed and the diagonals of the resulting indentation are measured from these the hardness number is calculated by dividing the load by the surface area of indentation. Hardness Test is discussed in this video and lab. Three common types of Hardness tests were introduced: Brinell, Rockwell and Vickers Tests. The difference o.TableofContents ListofFigures ix ListofTables xii 1.Introduction 1 2.RockwellHardnessTest 2 2.1Significanceofthetest 2 2.2Rockwellindentationtestprinciple 2 2 .
Hardness Value: A measurement of the material's hardness is provided by the test's Vickers hardness number. Greater hardness is indicated by a higher HV. Vickers hardness values are a useful tool for comparing the hardness of various materials. When choosing materials for engineering purposes, this information is helpful. (III) Theory: The Brinell Hardness Test is used to determine the Hardness Number of hard, moderately hard, and soft material E.g.: Brass, Br onze, Aluminum, Gold, and Copper.
types of hardness testing methods
This type of hardness is related to elasticity. The device used to take this measurement is known as a scleroscope.[3] Two scales that measures rebound hardness are the Leeb rebound hardness test and Bennett hardness scale. Mechanisms and theory[edit] A representation of the crystal lattice showing the planes of atoms.This study tested the hardness of aluminum and low-carbon steel using Rockwell hardness testing. Hardness testing measures a material's resistance to plastic deformation by indentation. The study found that low-carbon steel has a higher hardness than aluminum, as steel required greater force to deform its crystal structure. Specifically, the average Rockwell hardness of .The Rockwell method is a static hardness testing method, which can be further characterised as follows: It is one of the standardised procedures (ISO 6508, ASTM E18). The process is used to test hardness in the macro range (test force >= 49.03 N), more precisely with a test force of 29.42 to 1471 N. It is a differential-depth method.1. ROCKWELL HARDNESS TEST 1. AIM: To determine the Rockwell Hardness of a given test specimen II. APPARATUS: Rockwell Hardness testing machine, Test specimen. III. THEORY: HARDNESS- It is defined as the resistance of a metal to plastic deformation against Indentation, scratching, abrasion of cutting.
To determine the hardness of various engineering materials using Rockwell hardness test. 2. To develop an understanding of suitable scale for hardness test specimens. THEORY Hardness is a measure of the resistance of a metal to permanent (plastic) deformation. The hardness of the metal is measured by loading an indenter into its surface.hardness test and the tensile test measure the resistance of a metal to plastic flow, and results of these tests may closely parallel each other. The hardness test is preferred because it is . THEORY Current practice divides hardness testing into two categories: macrohardness and microhardness. Macrohardness refers to testing with applied .
Discussion of Theory Hardness Test and Melting Point of Grease - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. Scribd is the world's largest social reading and publishing site.a. Yes I agree. The elastic modulus and the ultimate strength can be identified using a hardness test. b. No I disagree. The Young's modulus can be found using hardness test but not yield strength. c. No I disagree. The young modulus and elastic characteristics of the material cannot be identified using a hardness test. d. Yes I agree.In the Rockwell hardness test, a differential-depth method, the residual depth of the indent made by the indenter, is measured.In contrast, the size of the indentation is measured in the Brinell, Vickers and Knoop optical test .
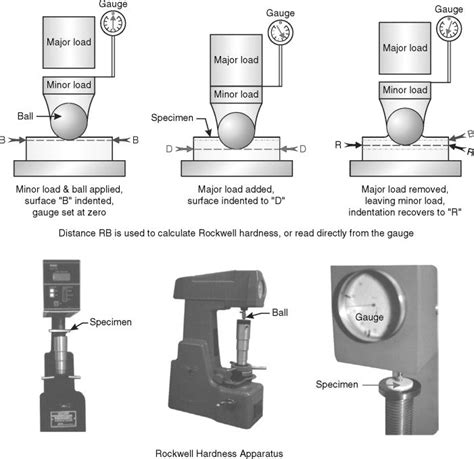
Theory: Refer to Mechanics of Material Laboratory manual for detail information. Summary of Theory: Vickers hardness test requires a diamond pyramid indenter with an included angle of 136o. This technique is also called a diamond pyramid hardness test (DPH) according to the shape of the indenter.The Rockwell hardness test is a indentation hardness test in which a diamond cone having an included angle of 120o and radius of curvature at the tip of 0.2mm, or a hardened steel or hard metal ball having a diameter of 1.5875mm for B, F, G and all 'T' scales or 3.175 mm for E, H and K scales are used.The indenter is forced into the surface of a test piece in two steps, initially a . After the preliminary test force has been applied for a short time, the dial gauge is set to zero (reference level). The actual hardness value can then be determined. Figure: Rockwell hardness test procedure. The actual test load F 1 is applied in addition to the preload and the indetor penetrates the material with the total force F=F 0 +F1 .
4. Record the Rockwell hardness number directly from the machine's display. 3. Vickers Hardness Test: The Vickers test utilizes a diamond pyramid indenter to create a square indentation. It's known for its high precision and ability to test a wide range of materials. Standard Sizes: Similar to Brinell, sufficient thickness is essential. The minimum Hardness is a mechanical property of materials. It is defined as the resistance of a material to deformation in indentation or scratching. There are many typ.
principle of hardness tester
The Brinell method has a test load range of 1 to 3000 kgf, which means that this method can be used for hardness testing in the low-load and, above all, macro ranges (conventional range). It is an optical method. This means that the size of indentation left by the indenter is measured to determine the hardness value of a test specimen.
Brinell hardness test is most commonly used to test materials that have a structure that is too rough or too coarse to be tested using other test methods, e.g., castings and forgings. In brinell testing machine the load is applied by a lever mounted on knife edges and carrying a hanger for suspending the required load.
The Rockwell method is a static hardness testing method, which can be further characterised as follows: It is one of the standardised procedures (ISO 6508, ASTM E18). The process is used to test hardness in the macro range (test force >= 49.03 N), more precisely with a test force of 29.42 to 1471 N. It is a differential-depth method.The hardness of metals can be tested by 12 different hardness tests and the Brinell Hardness test is the oldest technique to measure the hardness of metals but is widely used. In this blog, we will discuss only Brinell Hardness test methods, including principle and theory, applications, advantages and disadvantages. 6. General types of hardness testing... Current practice in USA divides hardness testing into two categories: Macrohardness: Refers to testing with applied loads on the indenter of more than 1 kg and material being tested are tools, dies and sheet material in the heavier gages(in large scale) Microhardness: Refers to testing with applied loads are 1 kg or below, .
load hardness tests vs depth
importance of hardness test
There's no point adjusting the winning score in practice mode.
hardness test theory|principle of hardness tester